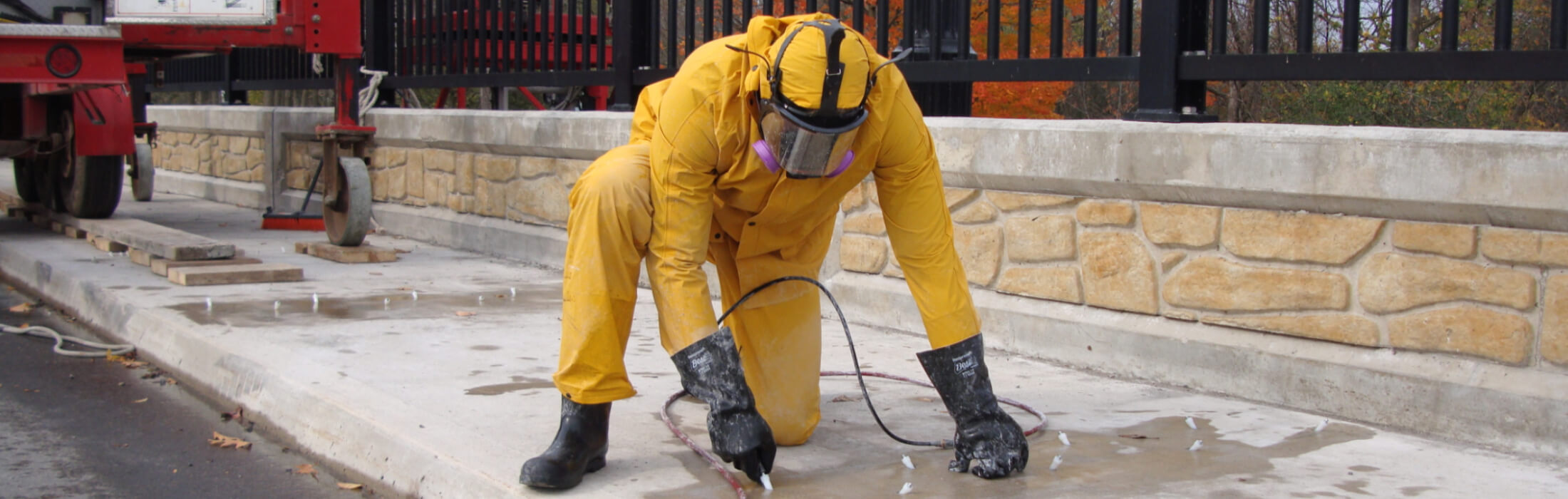
EPOXY INJECTIONS (STRUCTURAL)
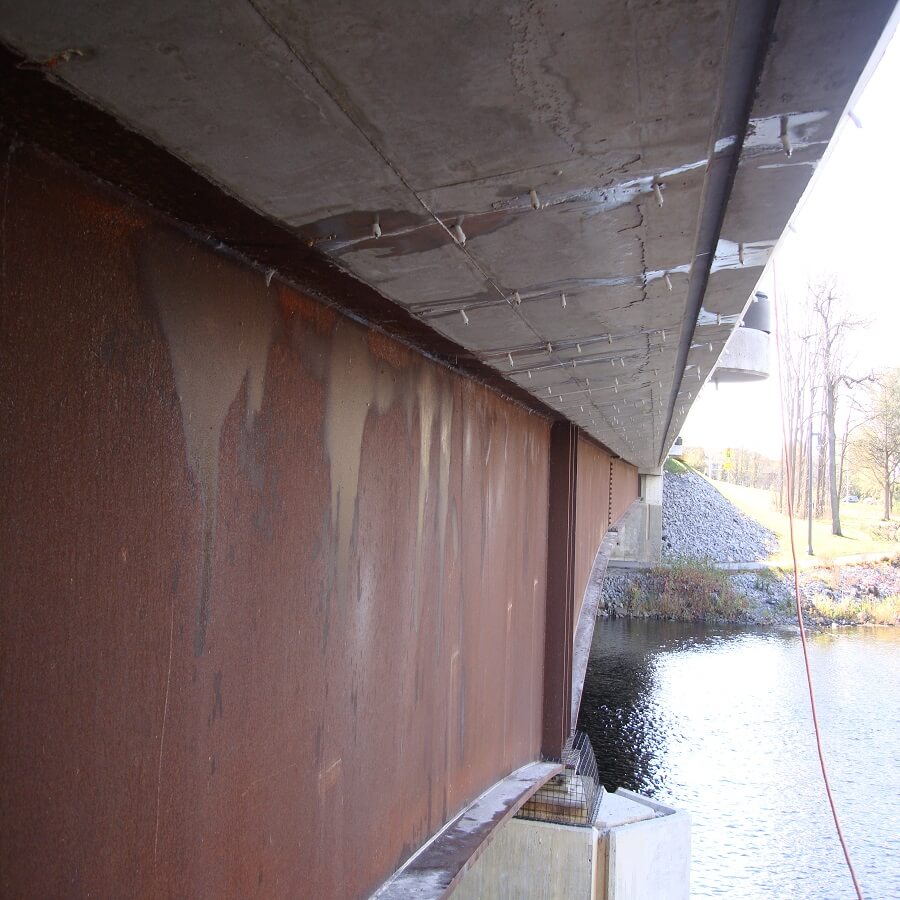
High strength epoxy is used where the concrete has been broken by tension and the crack has compromised the strength of the structure. Epoxy injection bonds or welds cracks as narrow as 0.002 inches together and its high tensile strength improves the structure strength. Epoxy will restore the structural integrity of the crack or defect in the concrete by filling the crack with a high-strength adhesive. This method consists of installing injection ports into drilled holes at close intervals along horizontal, vertical or overhead cracks and pressure-injecting epoxy. Cracks injected with epoxy needs to be dormant and not actively leaking.
POLYURETHANE INJECTION (WATERPROOFING)
Urethane crack injection is an effective way to seal cracks as narrow as 0.002 inches in a concrete structure to stop the flow of water. This repair option is primarily used to stop water leaks and consists of injecting a reactive resin into cracks that combine with water to form an expanding gel that chokes off the leak and seals the crack. Hydrophobic resins will chase the water and penetrate into tight micro-cracks and pores of the concrete creating a firm bond to the wet concrete. Also, cured polyurethanes are flexible and will tolerate future crack movements. This repair option is a permanent repair and works with either active or dormant crack and can be used for injection tubing systems, which are installed at concrete boundaries between new and old slabs.
GROUTING
Cementitious grouting is the process where a fluid cementitious grout is pumped under pressure to fill forms, voids, and cracks. Pressure grouting using a relatively low-cost cementitious material is used to fill cracks and voids where large volumes of material are required or where high service temperatures are anticipated. Cementitious grouting is also used to bond and protect rock anchors in concrete or rocks. OCFS has a wide assortment of specialized equipment for cementitious pressure grouting.